 |
| Domain Name |
What is the difference between a URL, Domain, Subdomain, Hostname etc.?
The abbreviation “URL” is short for “Uniform Resource Locator” and is commonly used to refer to a website or internet-address, while the actually intended goal is usually a directory or a specific path.
Contents
- The structure and components of a URL
- General language use
The structure and components of a URL
 |
| What is a URL? |
A URL is usually made up of several parts. To understand the structure and the components, we will dismantle the following example URL:
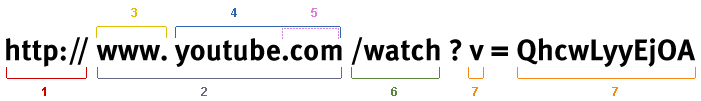
Structure and components of the URL http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QhcwLyyEjOA
- The Protocol in use – in this case: HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- There are also other protocols like HTTPS, FTP and so on.
- The Host or Hostname: www.youtube.com
- The Subdomain: www.
- The domain name (Domain): youtube.com
- The Top-Level-Domain (a web-address suffix): .com
- (also known by the shorthand TLD)
- The Path: /watch
- A path will usually refer to a file or folder (directory) on the
webserver (for example “/folder/file.html”)
- Parameter and value: v (Parameter), QhcwLyyEjOA (Parameter value)
- Parameters are initialised by the “?” inside the URL.
In our example, the parameter name is “v” and its value is “QhcwLyyEjOA” (Parameter name and Parameter value always have the same structure: Parametername=Parametervalue)
General language use
If we talk about a URL, we usually mean the concrete path to a directory (http://www.domain.com/a-directory/) or a file (http://www.domain.com/documents/study.pdf) on a website.
It is, of course, not completely wrong to talk about a URL and simply mean the host- or domain name of a website, but we should try to use the correct terminology.
Website:
 |
| Website Address |
A
site or
website is a central location of various web pages that are all related and can be accessed by visiting the home page using a browser.
How to open a website
To view a website requires a browser (e.g., Internet Explorer, Edge, Safari, Firefox, or Chrome). For example, you are reading this web page using a browser. Once in a browser, you can open a website by entering the URL in the address bar. For example, typing
https://www.youtube.com opens the YouTube home page. If you don't know the URL of the website you want to visit, you can use a search engine to find the website on the Internet.
What is the difference between a website and web page?
A website refers to a central location that contains more than one web page or a series of web pages. For example, Computer Hope is considered a website, which contains thousands of different web pages, including the page you're reading now.
In the above
URL example, the website is computerhope.com and the web page is "url.htm" and is always the last part of the URL.
Who creates websites on the Internet?
Any business, government, or person can create a website on the Internet. Today, the Internet consists of billions of websites created by billions of different people. You can even create a website or blog on the Internet.
Blog:
Weblog
A weblog or blog, is a listing of text, images, or other objects that are arranged in a chronological order that first started appearing in 1998. Blogs are often maintained and run by a single individual, updated daily, or contain personal remarks about a topic, a personal ramble, or an update on the person's life. In many ways, many weblogs are like a personal journal or a look into another individual's life and can be a way to learn about people, events, places, and more from people around the world.
Some examples of software and services you can use to create and start personal weblogs include Blogger, Manila, Movable type, LiveJournal, Radio Userland, Typepad, WordPress.
Tip: With the popularity of social networking sites like Facebook and Twitter many people have also moved from doing blogs to making posts in their social network.
























